<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jvnet.hudson.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>javanet-uploader</artifactId>
<version>1.5</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Optional dependencies
By default, dependencies are mandatory — if any of the dependencies are unavailable then the plugin will be disabled and can not be used.
However, this is just the default. It is possible to declare dependencies to other plugins as optional. In this way, even if some of the optional dependencies are unavailable, the plugin will continue to be loaded and executed.
To declare an optional dependency, add the <optional/> tag to the declared dependency in the plugin pom.xml.
If any of the classes in the unavailable optional dependencies are used in the plugin a NoClassDefFoundError will be thrown.
It is still your responsibility to cope with these errors (although Jenkins itself does some of this handling.
If your particular extension fails to load with LinkageError because of a missing dependency, it will gracefully disable just that extension and move on to try instantiating other extensions.
You can mark your extension as an optional extension by changing the @Extension annotation to @Extension(optional = true) and Jenkins doesn’t log any class loading errors when reading it.
@Extension(optional = true)
public static class YourDescriptor extends Descriptor<YourDescribable> {
@Override
public String getDisplayName() {
return "YourDisplayName";
}
}To determine if an optional dependency is installed, the Jenkins.getPlugin(String) method can be used.
if (Jenkins.getInstance().getPlugin("javanet-uploader") != null) {
// use classes in the "javanet-uploader" plugin
}Plugin statuses and behaviors
| Status | getPlugin("dependee") != null | getPlugin("dependee") .getWrapper().isEnabled() | Load class from your plugin |
|---|---|---|---|
Not installed |
false |
NPE |
Fail |
Installed without restart |
true |
true |
Succeed |
Installed without restart before your plugin |
true |
true |
Succeed |
Installed |
true |
true |
Succeed |
Uninstalled - not restarted |
true |
true |
Succeed |
Disabled - not restarted |
true |
false |
Succeed |
Disabled |
false |
NPE |
Fail |
Code causes class loading
When your plugin optionally depends on another plugin, you have to access classes in the other plugin only when you have checked the plugin is installed.
In most cases, you can do that by testing the plugin is installed before executing code that accesses optionally loaded plugin classes.
However,there are cases when your class causes loading of other classes at class instantiation or through reflection calls.
For example, Descriptor#<init> calls Class#getMethod("getDescriptor") and often causes those cases.
Contained in public method declarations
-
Classes in public method declarations will be loaded.
-
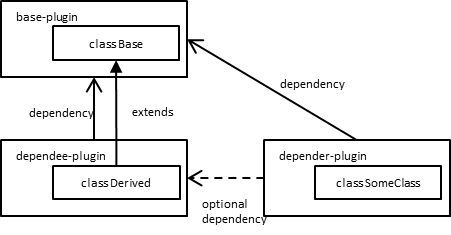
Any of following public method declarations cause Derived to be loaded when SomeClass is instantiated, or someone calls
SomeClass#getMethodand so on. If dependee-plugin is not installed, it causesNoClassDefFoundErroreven thoughdoSomething1()anddoSomething2are never executed.
public class SomeClass {
// They cause loading Derived even without execution.
public Derived doSomething1() {
// dosomething...
}
public void doSomething2(Derived arg0) {
// dosomething...
}
}-
It is best to not use classes from optional plugins in method declarations.
-
There might be cases even non-public (protected or private) method declarations cause class loading.
-
Upcasting
-
If there are codes upcasting to the base class, the derived class will be loaded.
-
Following code cause Derived loaded when
SomeClassis instantiated, or someone callsSomeClass#getMethodand so on. If dependee-plugin is not installed, it causesNoClassDefFoundErroreven thoughdoSomething()are never executed.
public class SomeClass {
public void doSomething() {
Derived d = getDrived();
Base b = (Base)d; // This causes loading Derived even without execution.
...
}
}-
Following code also cause loading
Derived.
public class SomeClass {
public void doSomething() {
Derived d = getDrived();
doSomethingImpl(d); // This causes loading Derived even without execution.
...
}
private void doSomethingImpl(Base b) {
// do something
}
}Upcasting not causing class loading
-
Upcasting to
Objectdoes not cause class loading. Following code does not cause loadingDerived.
public class SomeClass {
public void doSomething() {
Derived d = getDrived();
Object b = (Object)d; // This causes loading Derived even without execution.
...
}
}-
Generic types are considered only when compiling, and ignored when execution. Following code does not cause loading
Derived.
public class SomeClass {
public void doSomething() {
Collection<Derived> dList = getDerivedList();
Base b = (Base)dList.get(0);
}
}